The Study of Heat Transfer: An Overview of Thermal Exchangers

Thermal transfer is a essential concept in numerous areas of science and engineering, impacting all aspects from everyday appliances to sophisticated industrial systems. At the core of efficient heat transfer are heat exchangers, devices designed to enable the transfer of heat energy between two or more liquids without mixing them. These adaptable components play a crucial role in enhancing energy efficiency, managing temperature, and guaranteeing the dependability of many applications across varied industries.
In this post, we will examine the complexities of heat exchangers, looking into their categories, designs, and functionalities. We will explain how they operate and underscore the major impact they have on multiple sectors, including heating, ventilation, and air conditioning, power generation, and renewable energy applications. By comprehending the significance of heat exchangers, their upkeep needs, and innovations shaping their evolution, we can value their essential role in maximizing energy use and promoting eco-friendliness in an increasingly energy-aware world.
Understanding Heat Transfer Devices
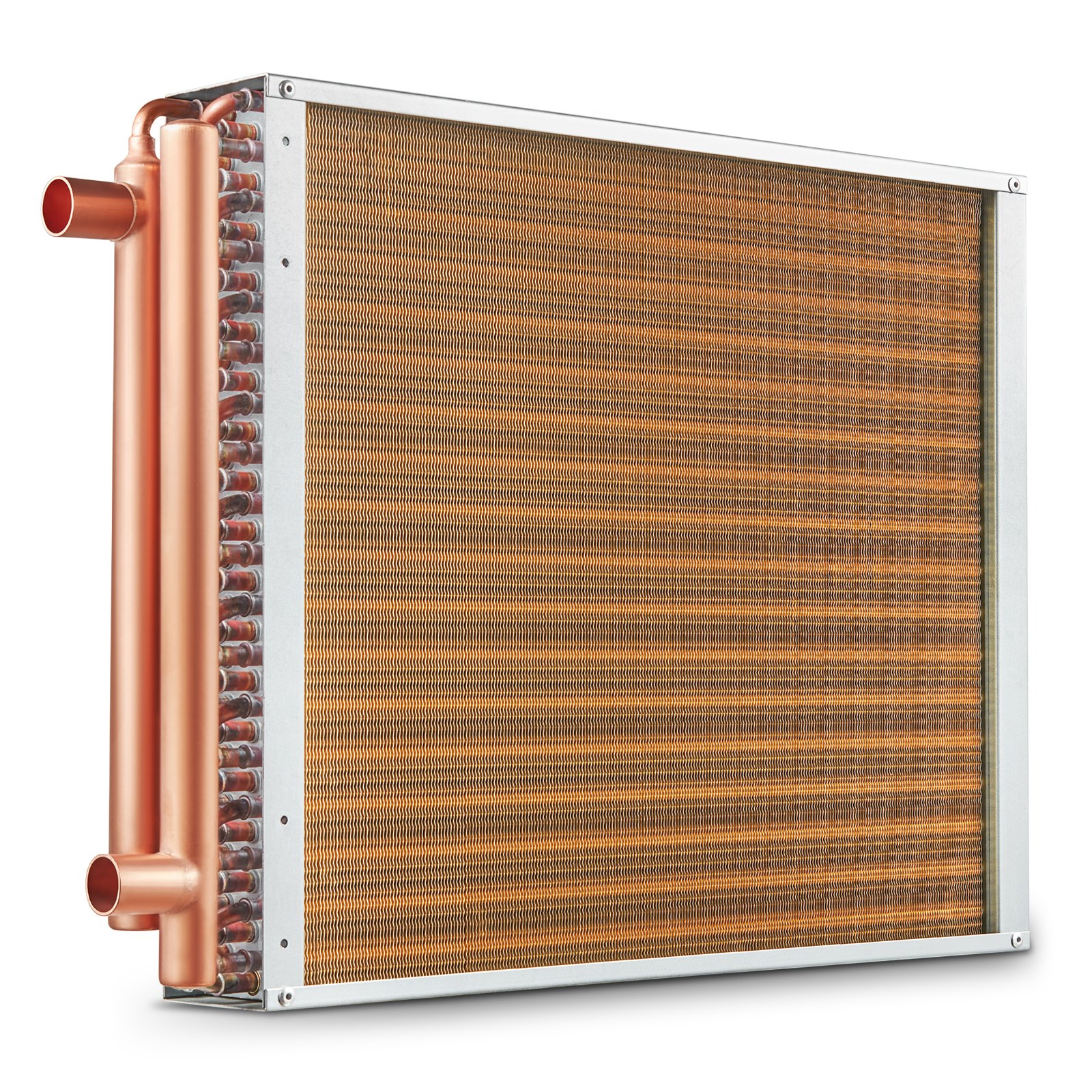
Thermal exchangers are essential components engineered to transfer thermal energy between two or more gases while avoiding mixing one another. Such fluids may consist of liquid substances, gaseous compounds, or an combination of the two, while they generally move in distinct routes. The main objective is to effectively absorb thermal energy from a hot liquid and convey it to a cooler one, thus optimizing the thermal energy use in various settings. This ability to manage thermal conditions makes heat exchangers essential in numerous industrial processes and HVAC systems.
The operational principle of a heat exchanger is based on the laws of thermodynamics, where heat naturally transfers from a higher temperature liquid to a lower temperature substance until such time as thermal balance is achieved. These devices are crafted with various surfaces and materials that enhance their heat transfer effectiveness. Typical designs include tube and shell, plate-type, and air-cooled types exchangers, each one suited for specific applications considering factors like spatial constraints, fluid characteristics, and required efficiency.
In the industrial landscape, heat exchangers play a important role in enhancing energy efficiency and sustainability. By reclaiming and utilizing again heat that would otherwise be wasted, these devices help lower operating costs and lessen environmental impact. Standard Exchange from power generation and chemical manufacturing to food and beverage industries, illustrating the versatility and importance of these systems in modern engineering. Managing their performance and maintenance is essential to ensure longevity and efficacy in such critical applications.
Uses and Efficiency of Heat Exchangers
Heat exchangers play a essential role across different industries, serving essential functions in processes that require heat control. In chemical manufacturing, they facilitate the exchange of heat between multiple fluids, ensuring that reactions occur at optimal thermal conditions. In the food and beverage sector, heat exchangers help maintain food safety by efficiently pasteurizing products, thus prolonging shelf life while retaining flavor. Additionally, in energy production, they are essential for managing the temperature of vapor and cooling systems, enhancing overall efficiency and stability.
The performance of heat exchangers is directly linked to their architecture and the substances used in construction. Different types exist, such as shell and tube, flat plate, and air-cooled exchangers, each offering distinct efficiency characteristics suited to particular applications. For instance, flat plate exchangers, known for their small-scale design and excellent thermal conductivity, are particularly effective in applications where there are space restrictions. As industries work to enhance energy efficiency, advanced designs continue to emerge, which improve heat transfer while minimizing energy loss.
Moreover, the role of heat exchangers in enhancing energy efficiency cannot be ignored. By capturing waste heat from industrial processes, they help diminish energy consumption and decrease operating costs. This factor is particularly significant in modern energy systems, where green practices has become a primary focus. The incorporation of cutting-edge technologies, such as digital monitoring and smart controls, also optimizes the effectiveness of heat exchangers, providing real-time data for maintenance and confirming they operate at optimal effectiveness.
Maintenance and Upcoming Developments
Effective care of heat exchangers is vital for ensuring their efficiency and durability. Regular inspections and cleaning are crucial to prevent fouling, which can significantly affect performance. Adopting a routine maintenance plan assists identify early signs of deterioration or failure, enabling for timely repairs and reducing unexpected downtime. Utilizing digital monitoring technologies can also enhance maintenance efforts by providing live data on heat exchanger performance, making it easier to pinpoint issues before they worsen.
As industries move towards more eco-friendly practices, upcoming trends in heat exchanger tech are expected to focus on improved efficiency and sustainable materials. Innovations such as compact heat exchangers and advanced designs aim to lower energy use and enhance thermal performance. Moreover, the development of new materials, including composite and organic options, may provide more sustainable alternatives while maintaining durability and efficiency in varied applications.
The transition towards renewable energy systems and greener technologies underscores the importance of heat exchangers in enabling efficient energy transfer and management. In sectors like HVAC, automotive, and chemical processing, current trends include the integration of advanced technologies that boost performance monitoring and predictive maintenance. As fields continue to evolve, the flexibility and efficiency of heat exchangers will play a pivotal role in meeting future energy demands and sustainability goals.
