Heat Exchanger Technology 101: Varieties , Uses , and Perks

Heat exchange systems are essential components in a wide range of industries, playing a important role in the transfer of heat between several fluids. These devices make it possible to effectively exchange thermal energy, improving processes in sectors as diverse as HVAC systems, energy generation facilities, renewable energy solutions, and food processing. Comprehending how heat exchangers function and the different types available can greatly impact energy performance and operational costs in any manufacturing setting.
In this article, we will investigate the fundamental concepts of heat exchangers, analyze the different types and their particular applications, and talk about the benefits they offer to modern technology. From the differences between shell and tube versus plate heat exchangers to the necessity of maintenance and innovations in design, we aim to provide a comprehensive overview. Whether you are a experienced engineer or a novice to the field, this guide will improve your understanding of heat exchangers and their vital role in eco-friendly practices.
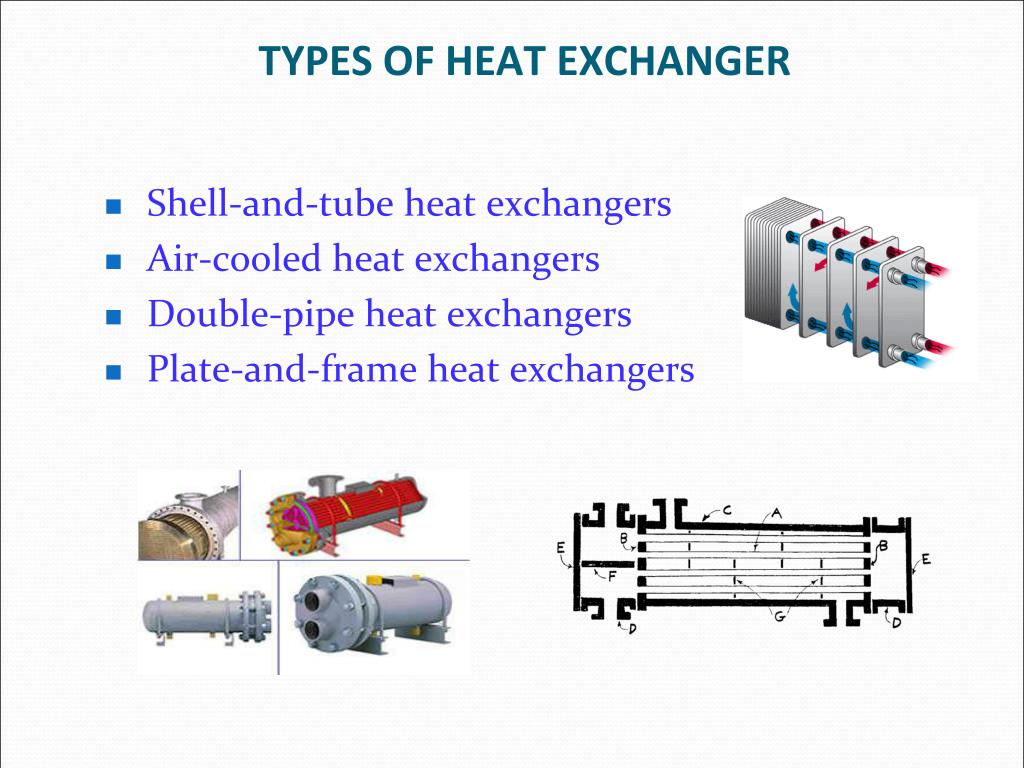
Types of Heat Exchangers
Heat exchangers are categorized into various types based on their construction and working principles. The primary types are active and passive heat exchangers. Active heat exchangers utilize external energy sources to boost heat transfer, while static types depend on natural circulation or conduction for transferring heat between fluids. Among these, the most utilized designs include shell and tube, flat plate, finned pipe, and air cooled heat exchangers, each designed for different uses and efficiencies.
Tube and shell heat exchangers consist of a series of tubes, where one fluid flows through the inner tubes and a second fluid flows around them within a shell. This design allows for high heat transfer efficiency and is commonly used in industries requiring robust and durable equipment, such as oil refining and power generation. Flat plate heat exchangers, on the other hand, have a stack of slim plates that create several channels for fluid flow, promoting high surface area contact and efficient heat transfer, making them ideal for food processing and HVAC applications.
Another notable type is the finned tube heat exchanger, which incorporates fins to boost the surface area for heat transfer, making them efficient in situations where room is limited. Air-cooled heat exchangers, which use air to cool the fluid, are commonly found in settings such as cooling systems and industrial cooling. Each of these heat exchanger types plays a crucial role in various industries, adapted to meet specific functionally demands and energy-saving goals.
Applications in Industry
Heat transfer devices play a crucial role in various industrial applications, contributing notably to efficiency of processes and energy efficiency. In the chemicals field, for example, these machines facilitate the transfer of heat between various operational streams, aiding in reactions and maintaining ideal temperatures. Specifically, they help regulate thermal energy in reactors, distillation columns, and various critical equipment, ensuring that processes run smoothly and safely.
In energy facilities, heat exchangers are essential for energy conversion. They assist in moving heat from burning gases to steam-producing water, generating steam that drives turbines for the production of electricity. Additionally, these devices help regulate thermal levels across the infrastructure, preventing thermal overload and enhancing overall effectiveness. Their design varies between coal plants, gas plants, and nuclear power plants, but their fundamental purpose remains the same: enhancing energy conversion rates while maintaining safety.
The food and beverage processing industry also is highly dependent on heat exchangers for pasteurization, temperature reduction, and storage methods. These exchangers ensure that products are thermal processed and cooled efficiently to meet regulatory standards without compromising the integrity of the product. By maintaining manufacturing equipment , they help prolong the longevity of products and maintain the quality of products, demonstrating the versatility and necessity of heat exchangers across multiple industrial fields.
Upkeep and Efficiency
Proper maintenance of heat exchangers is vital for guaranteeing maximum performance and efficiency. Regular inspections and maintenance help prevent fouling, which can substantially reduce heat transfer effectiveness. Consistently scheduled maintenance protocols should include the examination of seals, gaskets, and overall structural integrity to detect any potential points of failure promptly. Implementing a systematic approach to upkeep not only prolongs the duration of the equipment but also minimizes unexpected downtimes and costly repairs.
In terms of effectiveness, well-maintained thermal exchangers contribute to energy savings across various systems. By making sure thermal exchangers operate at peak performance, organizations can reduce their energy consumption and operational costs. For example, clean heat exchange surfaces encourage better thermal conductivity, which means that less energy is wasted in the heating or cooling processes. This energy conservation is particularly valuable in industries where energy costs make up a substantial portion of business budgets.
In conclusion, the link between upkeep and efficiency is obvious; proper upkeep leads to consistent performance. By adopting plans for preventive upkeep, facilities can enhance thermal exchanger reliability while simultaneously achieving sustainability goals. Such foresight in care and management not only improves the function of the heat exchangers themselves but also strengthens the sustainability of the entire industrial operation.
